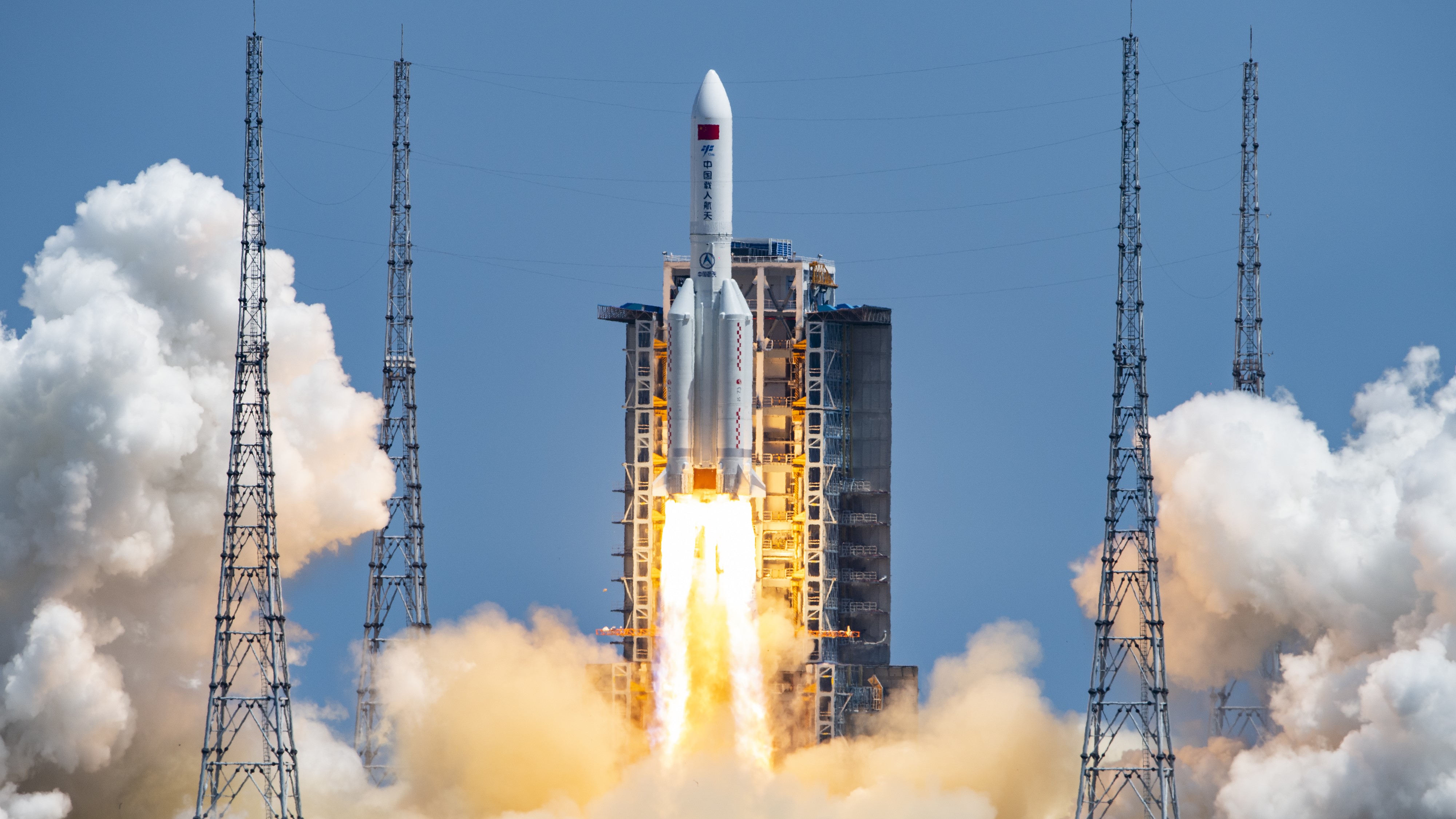
China has once again opted to let a huge rocket stage fall back to Earth on its own. The decision, the third time the country has opted not to control the disposal of the first stage of the Long March 5B rocket, once again puts China under scrutiny from space debris trackers after similar uncontrolled falls in 2020 and 2021. Jonathan McDowell, an experienced tracker of these events at the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, said U.
S. Space Command orbital data is showing the 21-ton stage floating on its own. "The inert .
. . core stage remains in orbit and was not actively deorbited," McDowell wrote (opens in new tab) on Twitter.
McDowell added (opens in new tab) that relative to U. S. launch providers, Americans "do a rather better job of upper stage disposal, and China on average a worse one.
" Related: China's Shenzhou 12 astronauts send back stunning images of Earth (photos) The U. S. military has not yet issued alerts on Twitter, either through Space Command or the 18th Space Defense Squadron that tracks re-entries.
Nor has Aerospace Corporation, which typically provides information on large human-made re-entering vehicles, discussed the matter on social media. Generally speaking, the risk of casualties from falling rocket stages are infinitesimally low, but the Long March 5B rocket body is particularly large. China launched the Wentian space station module on Sunday (July 24) at 2:25 a.
m. EDT (0625 GMT or 2:25 p. m.
Beijing time). Wentian safely docked with the Tiangong space station, as planned. A recent Nature Astronomy paper points out that the practice of letting huge stages make uncontrolled falls to Earth creates "unnecessary risk," and that China is not alone in the practice despite international guidelines for falling space debris mitigation.
The United States and most of the major international space agencies have practices governing how to deal with the risk of rocket stages. The American government, for example, governs its falls under Orbital Debris Mitigation Standard Practices (opens in new tab) . The practices require that risk of casualties from a re-entering rocket are below a 1-in-10,000 threshold, but the article notes this is not followed every time.
The U. S. Air Force waived the requirements for 37 of its 66 launches between 2011 and 2018, "on the basis that it would be too expensive to replace non-compliant rockets with compliant ones," the article stated.
NASA waived these casualty requirements seven times between 2008 and 2018, including an Atlas V launch in 2015 of the Magnetospheric Multiscale Mission that carried a casualty risk of 1 in just 600, the article added. The authors said it's important to remember this as both the Biden administration and NASA have condemned China's practices in past years. "There is no international consensus on the acceptable level of risk, and other spacefaring states — including the USA — make similar choices concerning uncontrolled reentries," the authors wrote.
The paper was led by Canadian political scientist Michael Byers, of the University of British Columbia. — China's Shenzhou 14 astronauts mark busy 1st month aboard Tiangong space station — China lays out big plans for its new Tiangong space station — 3 Chinese astronauts arrive at Tiangong space station for 6-month stay Since most uncontrolled rocket bodies launch near the equator, it's cities in the Global South that appear to bear disproportionate risk. The authors say that latitudes including Jakarta (Indonesia), Dhaka (Bangladesh), Mexico City, Bogotá (Columbia) and Lagos (Nigeria) have three times the risk of a re-entering rocket body than Washington, D.
C. , New York, Beijing and Moscow. The authors add that national governments with populations "at disproportionate risk by uncontrolled rocket bodies" should call for negotiations, non-binding resolutions or treaties to "create meaningful consequences for non-compliance and thus eliminate the risks for everyone.
" China, however, mostly works independently in space and NASA is not allowed to "engage in any bilateral activities with China or Chinese-owned companies," according to the agency (opens in new tab) . The country has also defended its practice of uncontrolled reentries, with China's foreign ministry saying in the past that the probability of issues "causing harm on the ground is extremely low. " Follow Elizabeth Howell on Twitter @howellspace (opens in new tab) .
Follow us on Twitter @Spacedotcom (opens in new tab) or Facebook (opens in new tab) . .